|
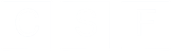
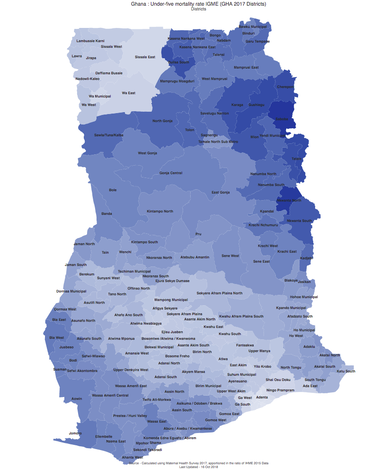
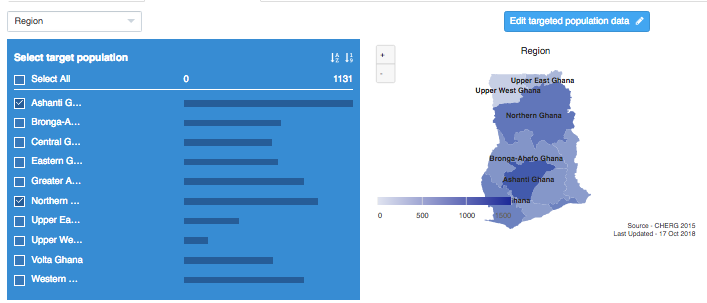
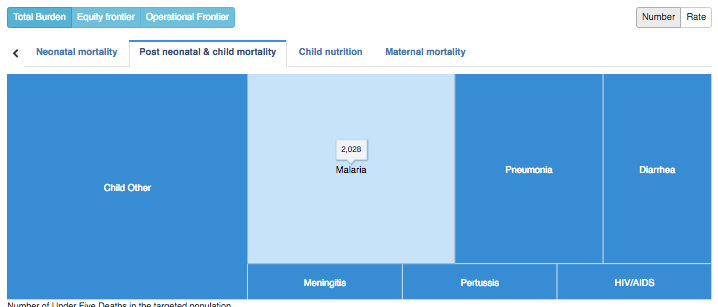
Seth Davis, Communications Officer, Community Systems Foundation Seeing the importance of a tool that provides this in-depth analysis of health sector priority areas, the Ministry of Health, Ghana recently collaborated with Community Systems Foundation technical staff to bring 2017 data into EQUIST. This was done by linking local data systems with the EQUIST database. From this training, Ministry counterparts also focused on the analysis of data in low performing districts, or those district that need the most assistance, by creating a specific dataset that visualises this data. With the ability to analyse data at the national, state and district level, EQUIST can now be used in Ghana to better understand the state of health sector progress across multiple scenarios and across nearly a decade worth of data. Ministry officials and policy planners can then use these scenarios to understand which interventions would create the highest reduction of deaths and which ones would be the most cost effective. Using the Most Recent Data in Ghana to Demonstrate the Impact of EQUIST Using Under 5 Mortality by Malaria as an indicator, the following analysis done in EQUIST will depict the impact that a malaria specific intervention could have in reducing the number of infant deaths by malaria. This will be mapped against the 2017 data that was entered into the system on 16-17 October 2018.To assist countries in the achievement of national priorities related to poverty eradication, under five child mortality rate and impact of malaria, tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS, the EQUitable Impact Sensitive Tool provides analysis of inequitable distribution of development results along with a scenario analysis function to access the impact of the removal of bottlenecks in the delivery of interventions. This helps national health programmes to prioritize interventions and geographical areas. [1] For this impact assessment on the areas in Ghana that have the highest mortality rate due to malaria, the visualisation above from EQUIST shows regions of Ashanti Ghana and Northern Ghana as the regions with high malaria deaths. These two regions have been selected as the target population for this impact assessment. EQUIST also has the ability to show the impact on the district level, however, this analysis will only focus on these two regions. Once an epidemiological priority is selected, users of EQUIST can see the number of under five deaths in the targeted population. Using malaria as an example, it can be seen that in 2017 there were 2,028 under five deaths related to malaria. In this regard, of the 8,212 post neonatal and child mortality deaths, nearly 25% were caused by malaria. Once this number is made available, specific interventions can be selected to address these large number of deaths due to malaria. 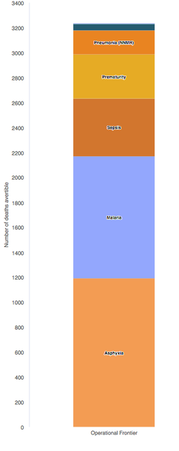 Following the selection of interventions, users can perform a bottleneck analysis to identify the bottlenecks of highest priority. This enables users to identify the causes of bottlenecks and helps to associate strategies that aim to address these causes. EQUIST then calculates what the improvements in the coverage of the intervention will be once the strategies identified are implemented. Following the completion of a bottleneck analysis in EQUIST, the tool generates the potential impact and cost due to projected improvement of coverage of the selected interventions. The impact on reduction of child mortality is arrived using the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health’s Lives Saved Tool (LiST). LiST “allows users to project the impacts of changes in coverage of health and nutrition interventions on child mortality using rigorous data and validated assumptions.” [2] From a LiST analysis, it can be seen that the total number of deaths averted would be 3,233. Of these avoided deaths, over 30% are from interventions dedicated to malaria prevention. Conclusion By utilizing EQUIST, over 60 countries within the database are able to analyse key priorities areas in their health sectors and determine specific interventions that will equate to meaningful impact. Following the conclusion of a specific scenario and a generation of an impact with EQUIST, users are also able to easily analyse desired outcomes and share their results with other registered users. In this regard, EQUIST provides a predictive analysis tool that aims to maximize lives saved by tailoring interventions to country-specific scenarios. [1] UNICEF Health Section, Programme. Early experiences with the Equitable Impact Sensitive Tool - EQUIST. December 2017. Page 16. Accessed at: http://www.equist.info/files/general_files/GLB_7834equist-working-paper-jan-2018.pdf
[2] UNICEF Health Section, Programme. User Guide: EQUItable Impact Sensitive Tool. April 2018. Page 13. Accessed at: http://www.equist.info/files/general_files/User_Guide.pdf
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Join the CSF data revolution webinar tomorrow!
COMMUNITY SYSTEMS FOUNDATION – EST 1963
+1 212 500 1335
data-driven sustainable development